What is Vitiligo?
What is Vitiligo?
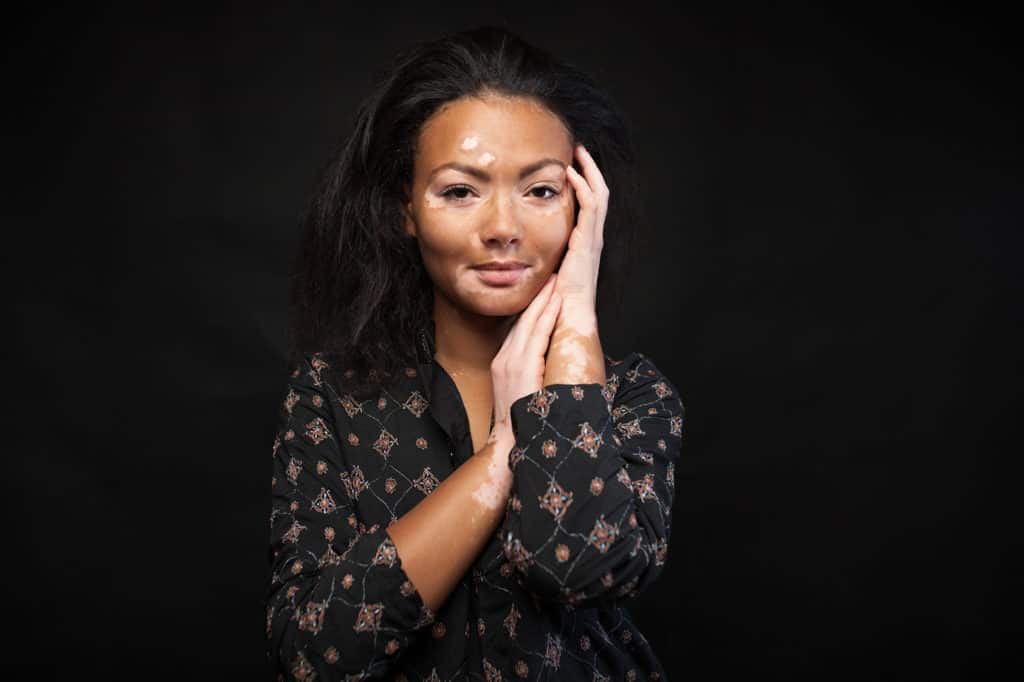
White spots on your skin? If you’re not sure if you have vitiligo (also called leukoderma or leucoderma), read this and evaluate these pictures of vitiligo.
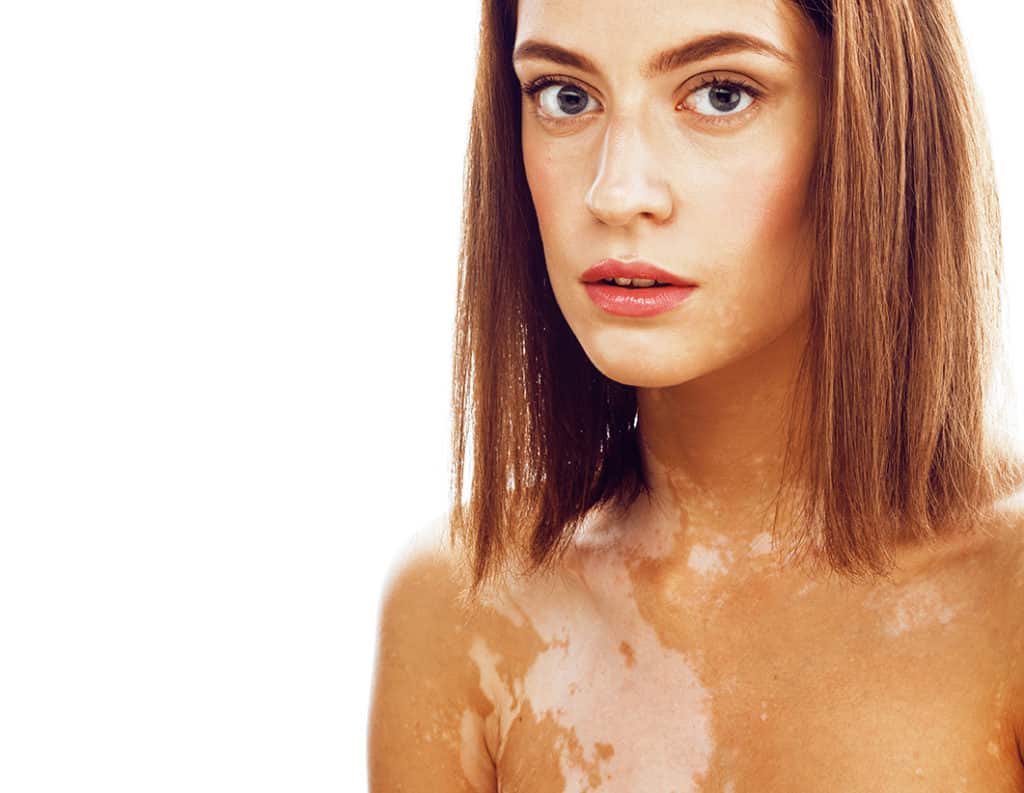

Vitiligo or leukoderma (also called leucoderma) is a condition where skin loses melanin – the pigment that colors skin, hair, and eyes. Vitiligo is characterized by bright white patches on the skin. There are different causes for these white spots on skin.
In 12 percent of cases, intense itching can occur at the site of skin depigmentation before a new vitiligo white spot develops. Vitiligo can occur at any age and on any part of the body. It’s not contagious. It affects all ages, ethnicities, and genders. There is no cure for vitiligo. However, it is treatable. Vitiligo treatments can slow the progression of new white patches appearing and also induce repigmentation (original color returning to skin). It is possible to repigment with current products that are both doctor prescribed and OTC.
According to the Mayo Clinic, there is a series of vitiligo symptoms.
Vitiligo signs include:
- Skin discoloration
- Premature whitening or graying of the hair on your scalp, eyelashes, eyebrows or beard (usually before age 35)
- Loss of color in the tissues that line the inside of your mouth and nose (mucous membranes)
- Loss of or change in color of the inner layer of the eyeball (retina)
- Discolored patches around the armpits, navel, genitals and rectum
The path of vitiligo is unpredictable. Skin turning white can start as a small area of pigment loss. People with vitiligo may have hair that turns gray early. Vitiligo patches can occur quickly or slowly. Patches may stop forming. In other cases, vitiligo patches can spread over the majority of the skin surface. Many people can go years without developing new spots. There are reports of people experiencing spontaneous repigmentation of the affected area of leucoderma.